These Foods May Help Repair Damaged DNA in Your Brain
Research has found that psychiatric disorders are linked to DNA damage in our brain.Anxiety is the most common mental disorder, affecting 40 million adults in the United States, according to Anxiety & Depression Association of America (ADAA). The global pandemic only exacerbated the situation. A March 2022 report by the World Health Organization said that the COVID-19 pandemic triggered a 25 percent increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide. The COVID States Project conducted a survey with more than 22,000 people across all 50 states and Washington, D.C in March of 2022. The survey reveals that the rate of depression varied greatly by age, while the rate stayed consistent among different age groups pre-pandemic. According to the survey, 50 percent of young adults aged 18 to 24 reported moderate or severe symptoms of depression, while only 9 percent of people 65 and older reported the same. In addition, research found that the COVID-19 vaccines might also contribute to mental disorders. U.K.’s COVID-19 specific Yellow Card reporting site identified a large range of neuropsychiatric complications as side effects of all the available COVID-19 vaccines. Even though science cannot explain the exact mechanisms causing mental disorders, it has proven that DNA damage and impaired repair of DNA damage is common in most psychiatric diseases. Oxidative DNA Damage The DNA in just one human cell can be damaged tens of thousands of times per day. Multiply that by the total number of cells, you get a quintillion (10 to the power of 18) DNA errors per day. DNA provides the blueprint for the proteins our cells need to function. Fortunately, our cells have different enzymes that repair different types of DNA damages. If left unrepaired, DNA damage can cause serious issues—including all sorts of degenerative diseases, cancers, and psychiatric disorders. A common cause of DNA damage is oxidation. Oxygen is essential for human life. Our brain consumes about 20 percent of our body’s total oxygen, making the brain cells more vulnerable to oxidative damage than other cells. A review by MIT researchers published in May 2022 states that oxidative DNA damage in brain tissues is observed in a variety of patients with psychiatric disorders, including anxiety disorders. The oxidative DNA damage is mainly caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). The common forms of DNA damage by ROS include single strand breaks (SSB) and double strand breaks. Research by East Tennessee State University in 2016 details the linkage between psychiatric disorders and high level of oxidative DNA damage in the brain. Studies reported “higher number of single and double stranded breaks in DNA along with oxidative damage with reduced DNA repair activity in patients with depressive disorder.” For instance, stress is often a predisposing factor in the development of Major Depressive Disorders (MDD). Under severe stress, the body begins to produce ROS that go unchecked, eventually resulting in MDD. Fruits and Vegetables May Decrease Oxidative DNA Damage Many studies have found that diets rich in fruits and vegetables may decrease oxidative DNA damage and enhance DNA repair. Researchers from Hong Kong Polytechnic University tested the ability of 9 fruits and vegetables to reverse DNA damage, including lemon, persimmon, strawberry, red apple, broccoli, celery, choy sum (a Chinese green leafy vegetable), lettuce, and orange. They found that low concentration extracts of lemon, persimmon, strawberry, red apple, broccoli, and celery displayed some DNA protection effects. Four dilutions of lemon extract was tested, and a 10 to the power of -4 extract was the most effective (left chart below). However, the effect of DNA protection was lost after boiling the extract for 30 mins (right chart below). The researchers concluded that the DNA protective agent in lemon, at least, is heat sensitive and that further study is required to identify the active ingredient(s) providing the protective effects. Other research also found that kiwifruit can protect human cells against oxidative DNA damage. Furthermore, extensive studies of various micronutrients show DNA protecting effects as well. Micronutrients are found in 30 to 40 essential vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids. Some 22 percent of all the enzymes need micronutrients to work, according to Rhonda Patrick, Ph.D., assistant scientist at Children’s Hospital Oakland Research Institute. One animal study conducted by scientists at the University of Oslo (Norway), University of Navarra (Spain), and Newcastle University (UK) found that deficiencies of methyl folate, niacin, zinc, vitamin A, and copper contributed to DNA damage. The good news is that through dietary supplementation of zinc, carotenoids, rutin, fruits, and other antioxidants, signs of reversal of DNA damage were observed in animals. The scientists also performed human intervention trials and found an increa

Research has found that psychiatric disorders are linked to DNA damage in our brain.
Anxiety is the most common mental disorder, affecting 40 million adults in the United States, according to Anxiety & Depression Association of America (ADAA). The global pandemic only exacerbated the situation. A March 2022 report by the World Health Organization said that the COVID-19 pandemic triggered a 25 percent increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide.
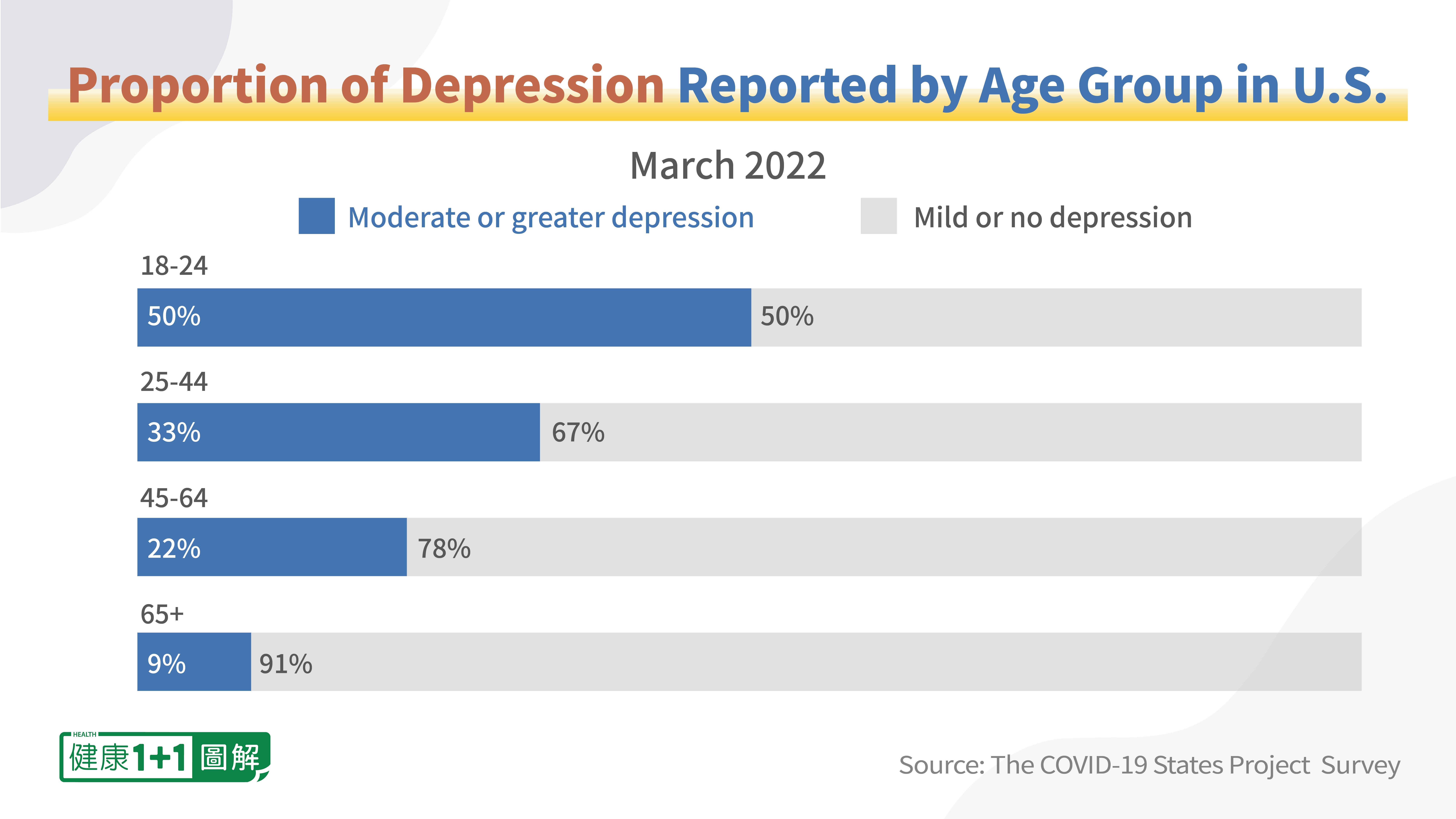
The COVID States Project conducted a survey with more than 22,000 people across all 50 states and Washington, D.C in March of 2022. The survey reveals that the rate of depression varied greatly by age, while the rate stayed consistent among different age groups pre-pandemic. According to the survey, 50 percent of young adults aged 18 to 24 reported moderate or severe symptoms of depression, while only 9 percent of people 65 and older reported the same.
In addition, research found that the COVID-19 vaccines might also contribute to mental disorders. U.K.’s COVID-19 specific Yellow Card reporting site identified a large range of neuropsychiatric complications as side effects of all the available COVID-19 vaccines.
Even though science cannot explain the exact mechanisms causing mental disorders, it has proven that DNA damage and impaired repair of DNA damage is common in most psychiatric diseases.
Oxidative DNA Damage
The DNA in just one human cell can be damaged tens of thousands of times per day. Multiply that by the total number of cells, you get a quintillion (10 to the power of 18) DNA errors per day.
DNA provides the blueprint for the proteins our cells need to function. Fortunately, our cells have different enzymes that repair different types of DNA damages.
If left unrepaired, DNA damage can cause serious issues—including all sorts of degenerative diseases, cancers, and psychiatric disorders.
A common cause of DNA damage is oxidation.
Oxygen is essential for human life. Our brain consumes about 20 percent of our body’s total oxygen, making the brain cells more vulnerable to oxidative damage than other cells.
A review by MIT researchers published in May 2022 states that oxidative DNA damage in brain tissues is observed in a variety of patients with psychiatric disorders, including anxiety disorders.
The oxidative DNA damage is mainly caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). The common forms of DNA damage by ROS include single strand breaks (SSB) and double strand breaks.
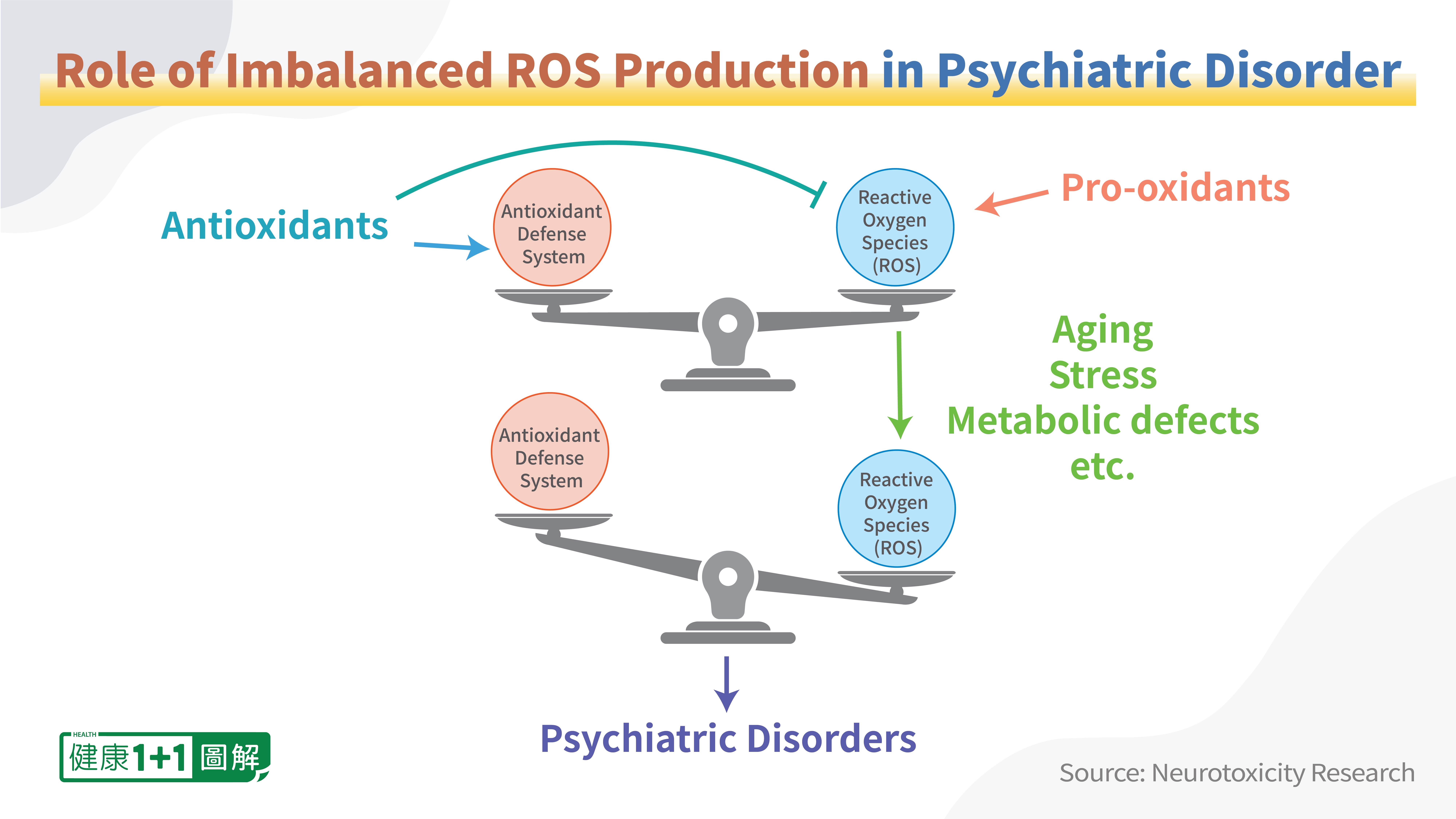
Research by East Tennessee State University in 2016 details the linkage between psychiatric disorders and high level of oxidative DNA damage in the brain. Studies reported “higher number of single and double stranded breaks in DNA along with oxidative damage with reduced DNA repair activity in patients with depressive disorder.”
For instance, stress is often a predisposing factor in the development of Major Depressive Disorders (MDD). Under severe stress, the body begins to produce ROS that go unchecked, eventually resulting in MDD.
Fruits and Vegetables May Decrease Oxidative DNA Damage
Many studies have found that diets rich in fruits and vegetables may decrease oxidative DNA damage and enhance DNA repair.
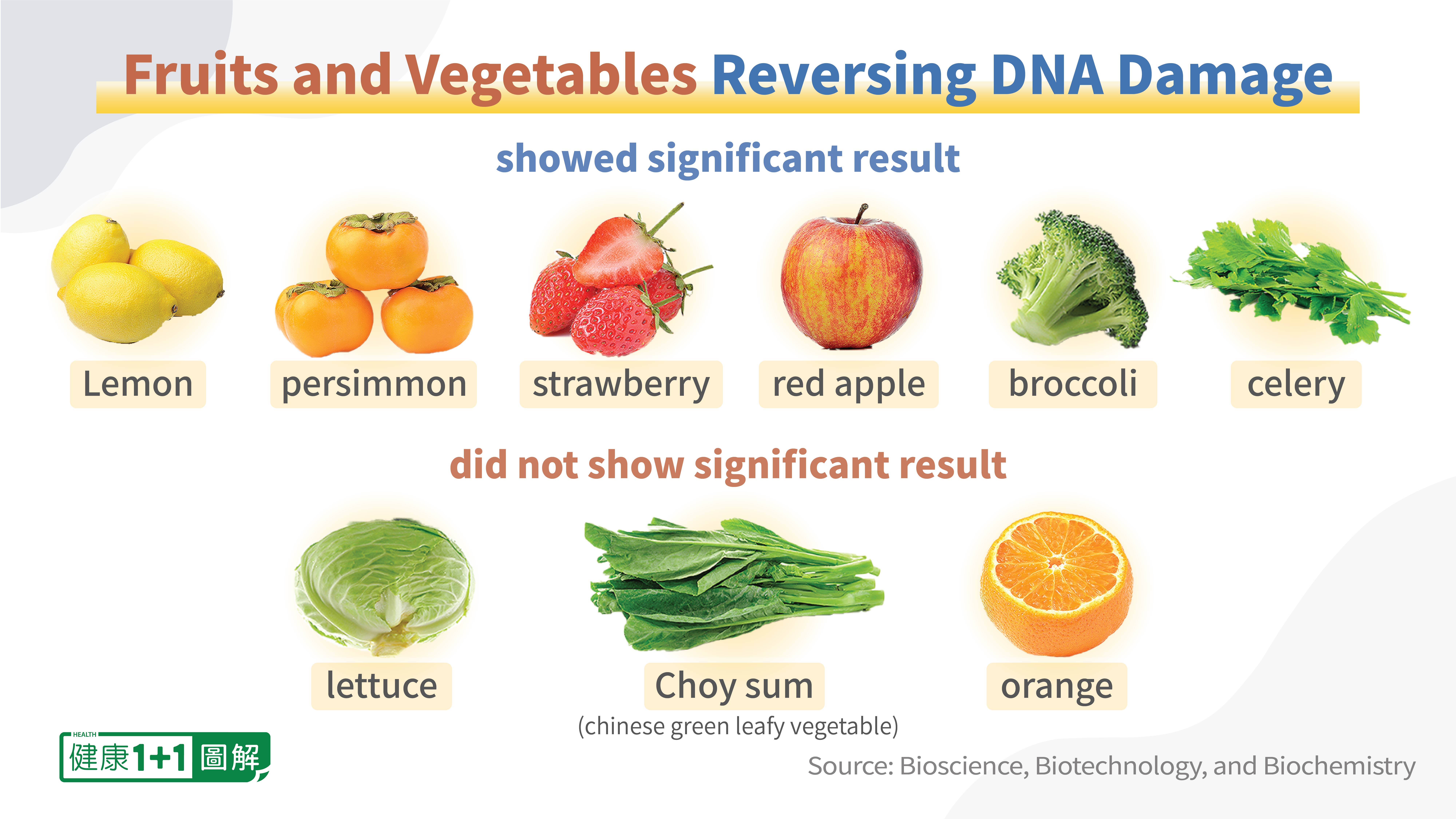
Researchers from Hong Kong Polytechnic University tested the ability of 9 fruits and vegetables to reverse DNA damage, including lemon, persimmon, strawberry, red apple, broccoli, celery, choy sum (a Chinese green leafy vegetable), lettuce, and orange.
They found that low concentration extracts of lemon, persimmon, strawberry, red apple, broccoli, and celery displayed some DNA protection effects.
Four dilutions of lemon extract was tested, and a 10 to the power of -4 extract was the most effective (left chart below). However, the effect of DNA protection was lost after boiling the extract for 30 mins (right chart below).
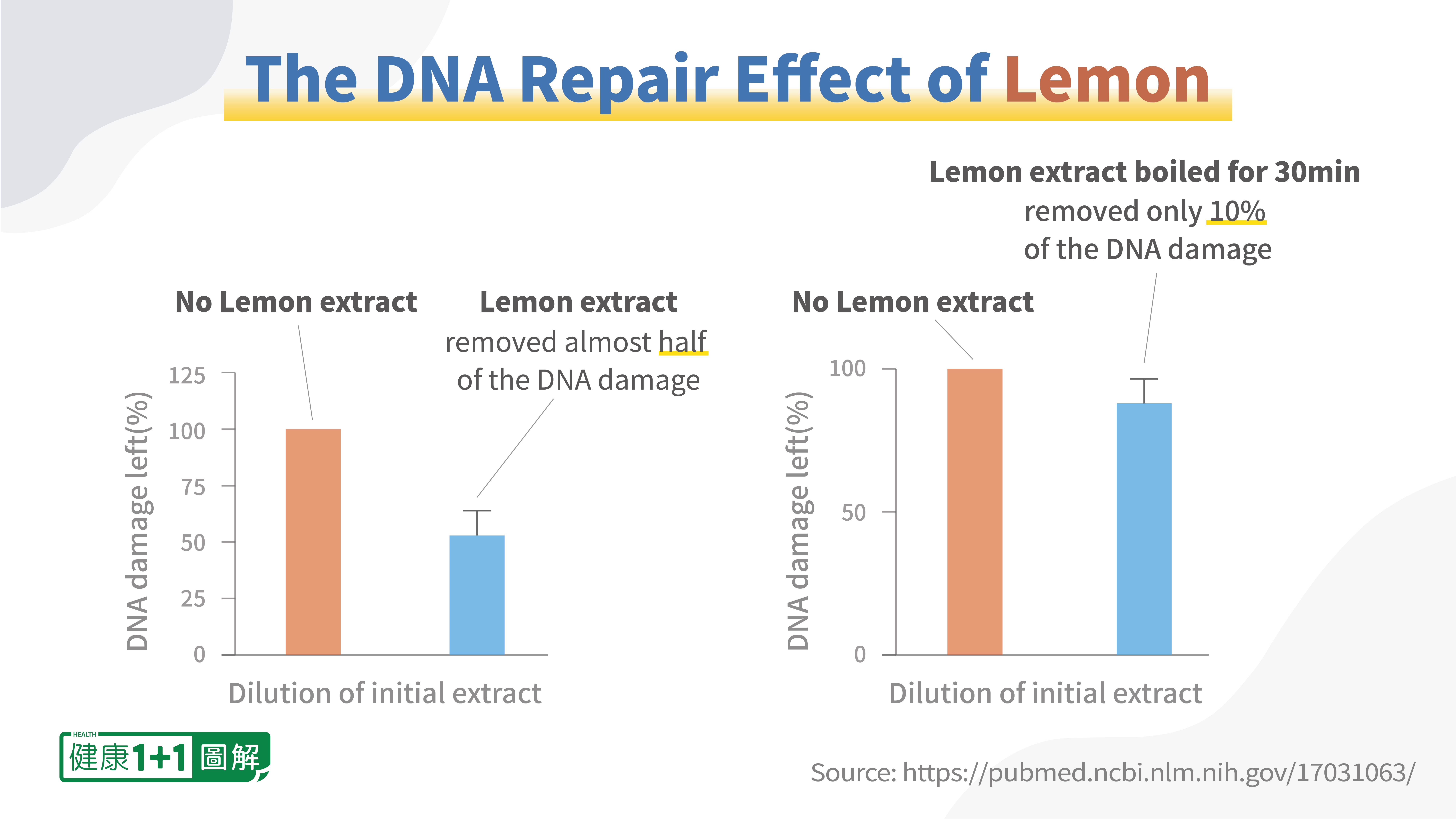
The researchers concluded that the DNA protective agent in lemon, at least, is heat sensitive and that further study is required to identify the active ingredient(s) providing the protective effects.
Other research also found that kiwifruit can protect human cells against oxidative DNA damage.
Furthermore, extensive studies of various micronutrients show DNA protecting effects as well.
Micronutrients are found in 30 to 40 essential vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids. Some 22 percent of all the enzymes need micronutrients to work, according to Rhonda Patrick, Ph.D., assistant scientist at Children’s Hospital Oakland Research Institute.
One animal study conducted by scientists at the University of Oslo (Norway), University of Navarra (Spain), and Newcastle University (UK) found that deficiencies of methyl folate, niacin, zinc, vitamin A, and copper contributed to DNA damage. The good news is that through dietary supplementation of zinc, carotenoids, rutin, fruits, and other antioxidants, signs of reversal of DNA damage were observed in animals.
The scientists also performed human intervention trials and found an increase in DNA repair activities from supplementation with coenzyme Q10, carotenoids, kiwifruit, B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, blueberry-apple juice, carrots, and other antioxidant-rich foods.
Because the trials participants varied greatly in their underlying health conditions, age, and lifestyle, the results are hardly comprehensive.
Nonetheless, we can conclude that diets rich in various fruits and vegetables can lead to increased DNA repair capabilities, and establishing healthy eating habits early in life is very important for our mental health.