These 6 Symptoms May Indicate Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a tumor that develops in the thyroid gland. Symptoms may include an enlarged thyroid gland, sore throat, and fatigue. The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased in recent decades, possibly due to advances in diagnostic techniques. According to 2020 figures, more than 950,000 people in the United States have thyroid cancer. 4 Main Types of Thyroid Cancer Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: As the most common type of thyroid cancer, this accounts for about 80 percent of all thyroid cancer cases. Papillary thyroid cancer is usually slow-growing, easy to treat, and has a favorable prognosis. Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular thyroid carcinoma accounts for about 15 percent of all thyroid cancers. These are like papillary thyroid carcinomas but have a higher rate of metastasis. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: These account for about 2 percent of all thyroid cancers. Medullary thyroid cancer arises in the C cells of the thyroid gland, which secrete a hormone called thyrocalcitonin. Medullary thyroid cancer usually does not absorb iodine and cannot be treated with iodine radiation. Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: This is the rarest type of thyroid cancer, accounting for about 2 percent of all thyroid cancer cases. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is malignant, fast-growing, and has a poor prognosis. 6 Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer Early stages of thyroid cancer are often asymptomatic, making it difficult to detect. However, when it enters the more advanced stage, some of the following symptoms may occur: Goiter: Thyroid cancer may cause a goiter, which is a usually painless swelling of the thyroid. A goiter is typically palpable and can sometimes cause a feeling of pressure in the neck. Sore throat or throat larynx: When thyroid cancer spreads to the throat, it may cause a sore throat, hoarseness, or larynx changes. Difficulty swallowing: When thyroid cancer enlarges, it may cause trouble swallowing. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck: When thyroid cancer spreads to the lymph nodes in the neck, it may cause swollen lymph nodes. Neck pain or pressure: When thyroid cancer grows, it may cause pain or pressure in the neck. Fatigue, weight loss, and loss of appetite: These symptoms are usually not the first symptoms of thyroid cancer, but they may appear when the cancer progresses to an advanced stage. Thyroid Cancer Risk Factors Currently, the cause of thyroid cancer is still not fully understood. However, the following are known risk factors that may be associated with developing thyroid cancer: Age: Thyroid cancer mainly occurs in people over 50 years old. Gender: Women are more likely to develop thyroid cancer than men. Genetic factors: If someone in the family has thyroid cancer, the risk of getting it may increase. Radiation: People who have previously received radiation therapy to the neck have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer. Diet: Insufficient or excessive iodine intake may increase the risk of thyroid cancer. Environmental factors: Some environmental pollutants may be related to thyroid cancer. It is worth noting that most thyroid nodules do not develop into thyroid cancer. Tips for Preventing Thyroid Complications Iodine intake: Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to synthesize thyroxine. Getting enough iodine can help prevent thyroid disease. However, consuming too much iodine may also lead to thyroid dysfunction. Getting your iodine from foods such as seaweed, seafood, salt, and milk is recommended. Avoid radiation exposure: Radiation therapy in the neck may increase the risk of thyroid cancer. Balanced diet: Appropriate nutritional intake helps to maintain good health and prevent diseases in general. Eating more vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and protein is recommended. Reduce consumption of high-sugar, high-fat, and processed foods. Regular checkup: Regular inspection of thyroid function and thyroid nodules will help detect thyroid diseases early and improve the treatment success rate. Avoid smoking: Smoking is harmful to your health and may also increase the risk of thyroid cancer. A study published in Scientific Reports in 2019 found that the more cotinine in the urine, the worse the thyroid function. Cotinine is a nicotine metabolite in tobacco, a key indicator of how much a person smokes. In short, good eating habits, avoiding radiation exposure, regular inspection of thyroid function, and monitoring changes in thyroid nodules are all essential to prevent thyroid diseases. If you’re concerned about whether you are at risk, speak with your doctor.
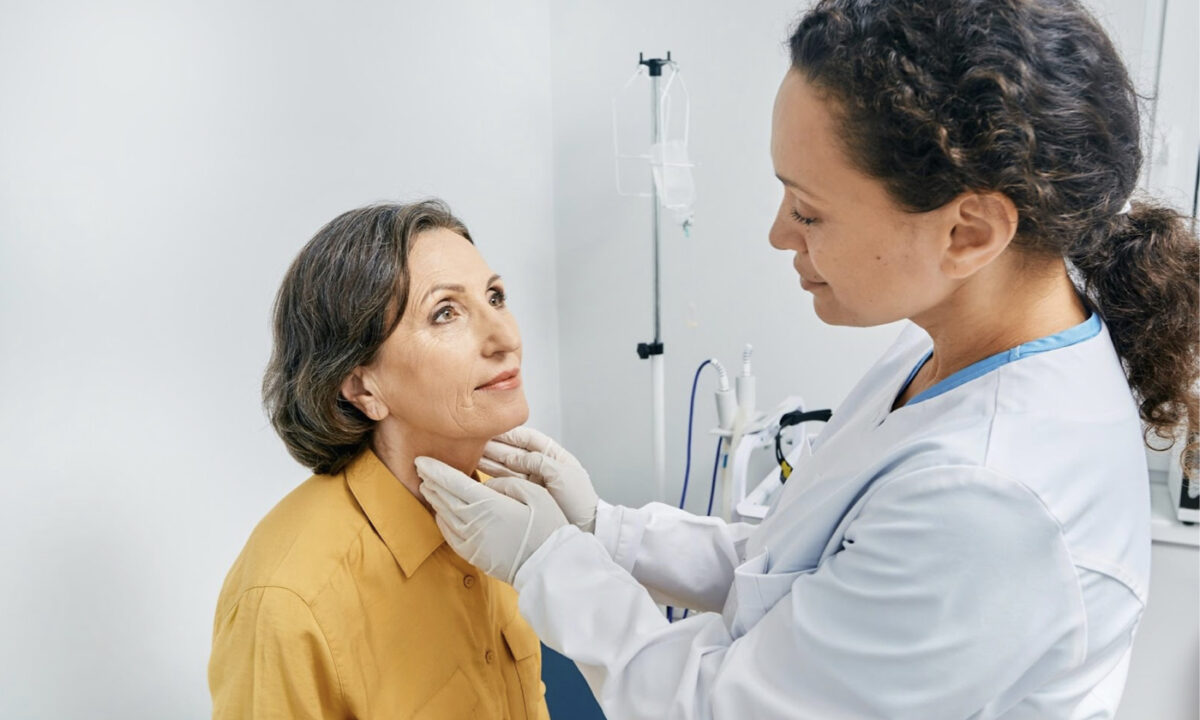
Thyroid cancer is a tumor that develops in the thyroid gland. Symptoms may include an enlarged thyroid gland, sore throat, and fatigue.
The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased in recent decades, possibly due to advances in diagnostic techniques. According to 2020 figures, more than 950,000 people in the United States have thyroid cancer.
4 Main Types of Thyroid Cancer
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: As the most common type of thyroid cancer, this accounts for about 80 percent of all thyroid cancer cases. Papillary thyroid cancer is usually slow-growing, easy to treat, and has a favorable prognosis.
Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular thyroid carcinoma accounts for about 15 percent of all thyroid cancers. These are like papillary thyroid carcinomas but have a higher rate of metastasis.
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: These account for about 2 percent of all thyroid cancers. Medullary thyroid cancer arises in the C cells of the thyroid gland, which secrete a hormone called thyrocalcitonin. Medullary thyroid cancer usually does not absorb iodine and cannot be treated with iodine radiation.
Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: This is the rarest type of thyroid cancer, accounting for about 2 percent of all thyroid cancer cases. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is malignant, fast-growing, and has a poor prognosis.
6 Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Early stages of thyroid cancer are often asymptomatic, making it difficult to detect. However, when it enters the more advanced stage, some of the following symptoms may occur:
- Goiter: Thyroid cancer may cause a goiter, which is a usually painless swelling of the thyroid. A goiter is typically palpable and can sometimes cause a feeling of pressure in the neck.
- Sore throat or throat larynx: When thyroid cancer spreads to the throat, it may cause a sore throat, hoarseness, or larynx changes.
- Difficulty swallowing: When thyroid cancer enlarges, it may cause trouble swallowing.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck: When thyroid cancer spreads to the lymph nodes in the neck, it may cause swollen lymph nodes.
- Neck pain or pressure: When thyroid cancer grows, it may cause pain or pressure in the neck.
- Fatigue, weight loss, and loss of appetite: These symptoms are usually not the first symptoms of thyroid cancer, but they may appear when the cancer progresses to an advanced stage.
Thyroid Cancer Risk Factors
Currently, the cause of thyroid cancer is still not fully understood. However, the following are known risk factors that may be associated with developing thyroid cancer:
- Age: Thyroid cancer mainly occurs in people over 50 years old.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop thyroid cancer than men.
- Genetic factors: If someone in the family has thyroid cancer, the risk of getting it may increase.
- Radiation: People who have previously received radiation therapy to the neck have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer.
- Diet: Insufficient or excessive iodine intake may increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
- Environmental factors: Some environmental pollutants may be related to thyroid cancer.
It is worth noting that most thyroid nodules do not develop into thyroid cancer.
Tips for Preventing Thyroid Complications
- Iodine intake: Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to synthesize thyroxine. Getting enough iodine can help prevent thyroid disease. However, consuming too much iodine may also lead to thyroid dysfunction. Getting your iodine from foods such as seaweed, seafood, salt, and milk is recommended.
- Avoid radiation exposure: Radiation therapy in the neck may increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
- Balanced diet: Appropriate nutritional intake helps to maintain good health and prevent diseases in general. Eating more vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and protein is recommended. Reduce consumption of high-sugar, high-fat, and processed foods.
- Regular checkup: Regular inspection of thyroid function and thyroid nodules will help detect thyroid diseases early and improve the treatment success rate.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking is harmful to your health and may also increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
A study published in Scientific Reports in 2019 found that the more cotinine in the urine, the worse the thyroid function. Cotinine is a nicotine metabolite in tobacco, a key indicator of how much a person smokes.
In short, good eating habits, avoiding radiation exposure, regular inspection of thyroid function, and monitoring changes in thyroid nodules are all essential to prevent thyroid diseases. If you’re concerned about whether you are at risk, speak with your doctor.