Pros and Cons of Guarana
If you enjoyed an energy drink recently, chances are it contained an ingredient known as guarana (Paullinia cupana). This plant, which is native to the Amazon rainforest, is the source of a substance associated with several health benefits, along with some cautionary notes.Guarana is a Brazilian plant highly regarded by natives for its healing qualities. The mature fruit of this climbing vine is bright red and the size of a coffee berry. The black seed in the berries is a significant source of the stimulants of caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline, as well as the antioxidants of catechin, saponin, and tannin. Health Benefits of Guarana Kills Bacteria: It’s been suggested that caffeine, along with the tannins or catechins found in guarana, is the source of guarana’s antibacterial properties. However, it’s been shown that guarana can kill Escherichia coli and Streptococcus mutans, bacteria that can cause diarrhea and tooth decay, respectively. Is High in Antioxidants: The various antioxidants found in guarana can help to fight cell and tissue damage related to free radical activity. Boosts Mental Energy and Focus. The high caffeine content of guarana (the seeds contain up to six times more caffeine than coffee beans) can help to increase mental energy, reduce fatigue, and improve focus. A study comparing people who took vitamins containing guarana and a placebo group found that those who consumed the guarana had less fatigue. Improves Memory and Learning Ability: Research has indicated that low doses of guarana (37.5 mg or 75 mg) improved learning ability and did so better than at higher doses. The authors suggested this shows that compounds other than caffeine are providing this benefit. In a study that compared the brain-enhancing compound ginseng with guarana, the use of the latter resulted in faster task performance times and better concentration. May Aid Weight Loss. The high caffeine content in guarana may accelerate metabolism by as much as 11 percent during a 12-hour period and thus aid in weight loss. Guarana’s impact on fat cell production, however, isn’t clear. Enhances Heart Health. You’ve probably heard of bad cholesterol (also known as low-density lipoprotein, or LDL). Guarana may reduce oxidation of this harmful substance, according to research. The antioxidants in guarana also may improve blood circulation. Improves Skin Health: Some cosmetics contain guarana, as the antioxidants may reduce skin damage associated with aging, minimize wrinkles around the eyes, and reduce sagging skin in the cheeks. Helps Digestive Problems: Do you experience constipation or diarrhea? The tannins in guarana may help with diarrhea since they are an astringent. Low doses of guarana can have an antidiarrheal effect. High doses (and thus more caffeine) may help with constipation. Cons of Guarana When consumed in amounts typically found in foods, or in the short-term for medicinal purposes, guarana is usually safe for most adults. In a 2019 review, the authors found that “guarana is not currently known to be associated causally with any serious health risks when consumed properly” and that “if guidelines for caffeine intake are respected,” using guarana is “not likely” to cause harm. However, high doses (more than 400 mg of caffeine daily), long-term use, or use by individuals who have certain health challenges may cause mild to severe side effects. These can include stomach irritation, nervousness, vomiting, and insomnia. Individuals who have specific conditions such as bladder control problems, diabetes, bleeding disorders, heart disease, high blood pressure, glaucoma, irritable bowel syndrome, or seizures may experience reactions associated with their health issues. Bottom Line Guarana is a natural remedy that may provide significant health benefits when used wisely. You can find guarana in energy drinks and as a supplement (pills, capsules, and powder), but in all cases, be aware of the caffeine content. Sources Bittencourt LS et al. The protective effects of guaraná extract (Paullinia cupana) on fibroblast NIH-3T3 cells exposed to sodium nitroprusside. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013 Mar; 53:119–25. Dulloo AG et al. Normal caffeine consumption: influence on thermogenesis and daily energy expenditure in lean and postobese human volunteers. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1989 Jan; 49(1):44–50. da Fonseca CA et al. Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of guarana (Paullinia cupana) in prokaryotic organisms. Mutation Research 1994 May; 321(3):165–73. Haskell CF et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-dose evaluation of the acute behavioral effects of guaraná in humans. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2007 Jan; 21(1):65–70. de Jesus NZ et al. Tannins, peptic ulcers and related mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Science 2012; 13(3):3203–28. Kennedy DO et al. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added gua
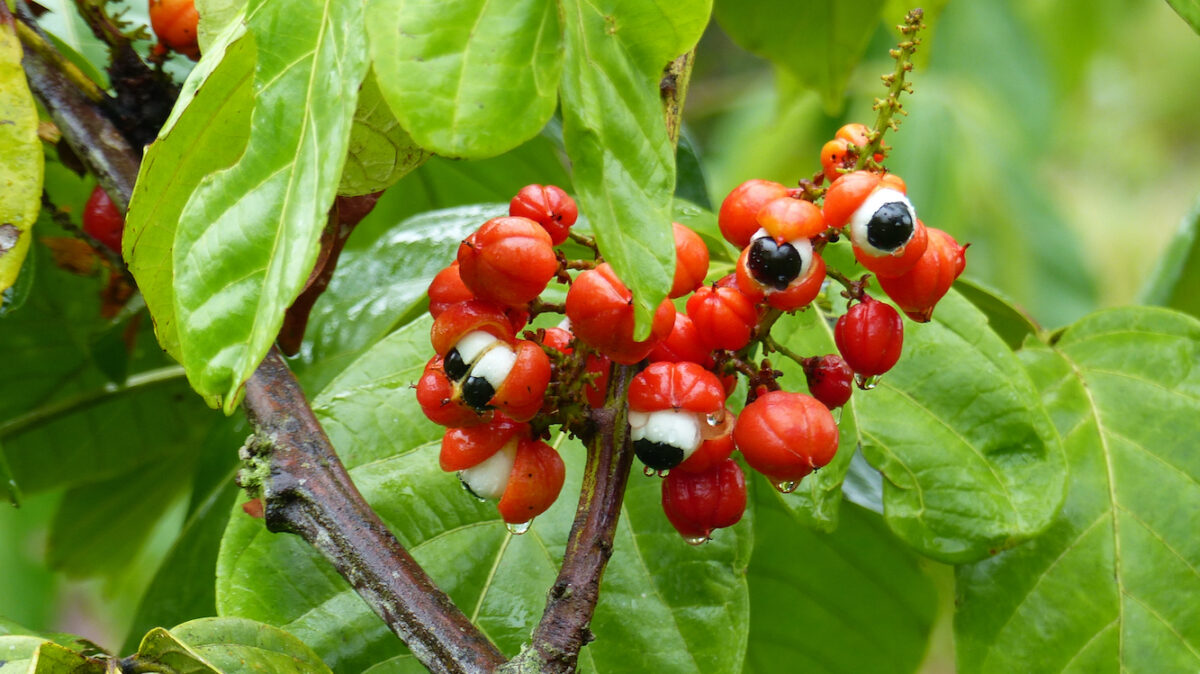

If you enjoyed an energy drink recently, chances are it contained an ingredient known as guarana (Paullinia cupana). This plant, which is native to the Amazon rainforest, is the source of a substance associated with several health benefits, along with some cautionary notes.
Guarana is a Brazilian plant highly regarded by natives for its healing qualities. The mature fruit of this climbing vine is bright red and the size of a coffee berry. The black seed in the berries is a significant source of the stimulants of caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline, as well as the antioxidants of catechin, saponin, and tannin.
Health Benefits of Guarana
Kills Bacteria: It’s been suggested that caffeine, along with the tannins or catechins found in guarana, is the source of guarana’s antibacterial properties. However, it’s been shown that guarana can kill Escherichia coli and Streptococcus mutans, bacteria that can cause diarrhea and tooth decay, respectively.
Is High in Antioxidants: The various antioxidants found in guarana can help to fight cell and tissue damage related to free radical activity.
Boosts Mental Energy and Focus. The high caffeine content of guarana (the seeds contain up to six times more caffeine than coffee beans) can help to increase mental energy, reduce fatigue, and improve focus. A study comparing people who took vitamins containing guarana and a placebo group found that those who consumed the guarana had less fatigue.
Improves Memory and Learning Ability: Research has indicated that low doses of guarana (37.5 mg or 75 mg) improved learning ability and did so better than at higher doses. The authors suggested this shows that compounds other than caffeine are providing this benefit. In a study that compared the brain-enhancing compound ginseng with guarana, the use of the latter resulted in faster task performance times and better concentration.
May Aid Weight Loss. The high caffeine content in guarana may accelerate metabolism by as much as 11 percent during a 12-hour period and thus aid in weight loss. Guarana’s impact on fat cell production, however, isn’t clear.
Enhances Heart Health. You’ve probably heard of bad cholesterol (also known as low-density lipoprotein, or LDL). Guarana may reduce oxidation of this harmful substance, according to research. The antioxidants in guarana also may improve blood circulation.
Improves Skin Health: Some cosmetics contain guarana, as the antioxidants may reduce skin damage associated with aging, minimize wrinkles around the eyes, and reduce sagging skin in the cheeks.
Helps Digestive Problems: Do you experience constipation or diarrhea? The tannins in guarana may help with diarrhea since they are an astringent. Low doses of guarana can have an antidiarrheal effect. High doses (and thus more caffeine) may help with constipation.
Cons of Guarana
When consumed in amounts typically found in foods, or in the short-term for medicinal purposes, guarana is usually safe for most adults. In a 2019 review, the authors found that “guarana is not currently known to be associated causally with any serious health risks when consumed properly” and that “if guidelines for caffeine intake are respected,” using guarana is “not likely” to cause harm.
However, high doses (more than 400 mg of caffeine daily), long-term use, or use by individuals who have certain health challenges may cause mild to severe side effects. These can include stomach irritation, nervousness, vomiting, and insomnia.
Individuals who have specific conditions such as bladder control problems, diabetes, bleeding disorders, heart disease, high blood pressure, glaucoma, irritable bowel syndrome, or seizures may experience reactions associated with their health issues.
Bottom Line
Guarana is a natural remedy that may provide significant health benefits when used wisely. You can find guarana in energy drinks and as a supplement (pills, capsules, and powder), but in all cases, be aware of the caffeine content.
Sources
Bittencourt LS et al. The protective effects of guaraná extract (Paullinia cupana) on fibroblast NIH-3T3 cells exposed to sodium nitroprusside. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013 Mar; 53:119–25.
Dulloo AG et al. Normal caffeine consumption: influence on thermogenesis and daily energy expenditure in lean and postobese human volunteers. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1989 Jan; 49(1):44–50.
da Fonseca CA et al. Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of guarana (Paullinia cupana) in prokaryotic organisms. Mutation Research 1994 May; 321(3):165–73.
Haskell CF et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-dose evaluation of the acute behavioral effects of guaraná in humans. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2007 Jan; 21(1):65–70.
de Jesus NZ et al. Tannins, peptic ulcers and related mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Science 2012; 13(3):3203–28.
Kennedy DO et al. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added guaraná (Paullinia cupana). Appetite 2008 Mar–May; 50(2–3):506–13.
Kennedy DO et al. Improved cognitive performance in human volunteers following administration of guarana (Paullinia cupana) extract: comparison and interaction with Panax ginseng. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 2004 Nov; 79(3):401–11
de Lima Portella R et al. Guaraná (Paullinia cupana Kunth) effects on LDL oxidation in elderly people: an in vitro and in vivo study. Lipids in Health and Disease 2013 Feb 8.
Lohsiriwat S et al.Effects of caffeine on anorectal manometric findings. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum 2008 Jun; 51(6):928–31.
Peixoto H et al. Anti-aging and antioxidant potential of Paullinia cupana var. sorbilis: Findings in Caenorhabditis elegans indicate a new utilization for roasted seeds of guarana. Medicines (Basel) 2017 Aug 15; 4(3):6
Peirano RI et al. Dermal penetration of creatine from a face-care formulation containing creatine, guarana, and glycerol is linked to effective antiwrinkle and antisagging efficacy in male subjects. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2011 Dec; 10(4):273–81.
Raman R. 12 benefits of guarana (plus side effects). Healthline 2018 13 Jun.
Smolarek PC et al. In vitro antimicrobial evaluation of toothpastes with natural compounds. European Journal of Dentistry 2015 Oct–Dec; 9(4):580–86.
Subbiah MT, Yunker R. Studies on the nature of anti-platelet aggregatory factors in the seeds of the Amazonian Herb Guarana (Paullinia cupana). International Journal of Vitamin and Nutrition Research 2008 Mar; 78(2):96–101.
WebMD. Guarana: uses, side effects, and more.