Headaches Are of Different Types and Each Has Some Health Reasons, Find Out More
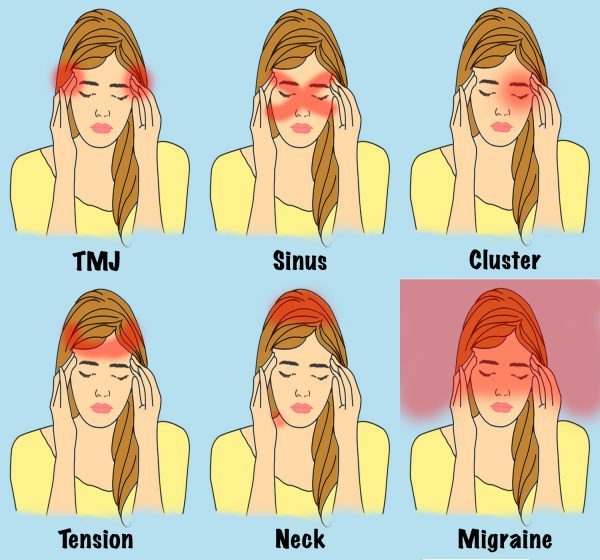
Knowing which kind of a headache you are experiencing can help you to treat it properly. Here, we have listed six types of headaches together with their symptoms in order to help you make a diagnosis.Although a headache is defined as a pain localized “in any region of the head,” in reality, there are many different types of headaches and thus there are different cures for them accordingly. Below are six types of headaches together with their description—once you know the type of headache, it’s easier to alleviate it with the right kind of treatment. #1. Temporo-Mandibular Joint (TMJ) Headaches This is a rare type of headache that usually occurs on the temples in front of the ears. It is a muscle-contraction type of pain, which can be accompanied by a painful “clicking” sound on opening the jaw. This headache is caused by malocclusion (poor bite), stress, and jaw clenching. A TMJ pain has been reported in almost 1 out of 10 people and at least half of the population in the United States. The best you can do is try to relax your jaws and tensed face muscles. Doctors can recommend the use of a bite plate, and if those methods don’t work, a correction of malocclusion may be necessary. #2. Sinus Headaches If you experience a gnawing pain over the nasal area, which intensifies throughout the day, it means you probably have a sinus type of headache. The pain occurs behind the cheekbones or browbone. Sinus headaches may be caused by acute infections. Usual treatment involves antibiotics, decongestants, or surgical drainage, if necessary. #3. A Cluster Headache A cluster headache happens when you feel pain in the vicinity of the eyes. The pain develops during sleep and may last several hours. Attacks occur every day for weeks or even months, then they disappear for up to a year. The exact cause is not yet known, and they might occur without any preliminary sign, like in the case of migraine. Possible factors include alcohol consumption and excessive smoking. Exercise and physical activities may help; reduction of alcohol and smoking would be helpful too. #4. A Tension Headache Symptoms of the tension-type headache include dull, non-throbbing pain across the sphere of the head. Tightness of the scalp or neck may accompany this pain. These occur one or two times per month on average to those who have episodic headaches. It may be caused by stress or a hidden depression. Short-term treatment will involve drugs and muscle relaxants prescribed by a doctor. Long-term treatment will involve learning relaxation techniques like meditation, quitting alcohol consumption and smoking, and learning more effective ways of coping with stress. #5. Neck Pains This pain is localized on the neck and nape. The pain gets worse when you move. It is caused by inflammation of the blood vessels of the head or bony changes in the structures of the neck. Short-term treatment will involve anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants prescribed by a doctor. Long-term prevention would require learning relaxation techniques and performing neck-muscle exercises. #6. Migraine Severe, one-sided throbbing pain, often accompanied by nausea, cold hands, and sensitivity to sound and light means that you are having a migraine. The causes of migraines are not entirely understood, but genetics may play a role. Many factors can induce a migraine, like menopausal hormones, weather changes, stress, and a change in altitude, to name just a few. A migraine attack can cause pains for several hours to days, and the pain can be quite disabling. About one-third of people experience an aura before the start of a migraine, according to Medical News Today. Migraines can occur in both adults and children. The attack frequency can be several times a week, or in some cases only once a year. Short-term treatment will involve analgesics and anti-nausea medications prescribed by a medic. Long-term preventive methods will include regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and learning positive ways of coping with stressful situations. Photo credit: Illustration – The Epoch Times Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Knowing which kind of a headache you are experiencing can help you to treat it properly. Here, we have listed six types of headaches together with their symptoms in order to help you make a diagnosis.
Although a headache is defined as a pain localized “in any region of the head,” in reality, there are many different types of headaches and thus there are different cures for them accordingly. Below are six types of headaches together with their description—once you know the type of headache, it’s easier to alleviate it with the right kind of treatment.
#1. Temporo-Mandibular Joint (TMJ) Headaches
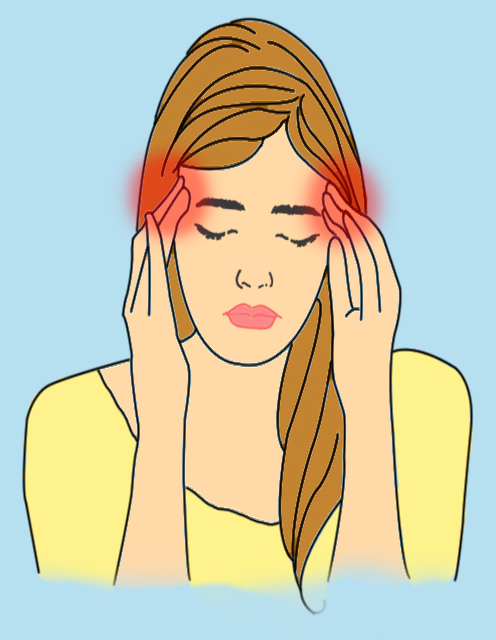
This is a rare type of headache that usually occurs on the temples in front of the ears. It is a muscle-contraction type of pain, which can be accompanied by a painful “clicking” sound on opening the jaw. This headache is caused by malocclusion (poor bite), stress, and jaw clenching.
A TMJ pain has been reported in almost 1 out of 10 people and at least half of the population in the United States.
The best you can do is try to relax your jaws and tensed face muscles. Doctors can recommend the use of a bite plate, and if those methods don’t work, a correction of malocclusion may be necessary.
#2. Sinus Headaches

If you experience a gnawing pain over the nasal area, which intensifies throughout the day, it means you probably have a sinus type of headache. The pain occurs behind the cheekbones or browbone. Sinus headaches may be caused by acute infections. Usual treatment involves antibiotics, decongestants, or surgical drainage, if necessary.
#3. A Cluster Headache
A cluster headache happens when you feel pain in the vicinity of the eyes. The pain develops during sleep and may last several hours. Attacks occur every day for weeks or even months, then they disappear for up to a year. The exact cause is not yet known, and they might occur without any preliminary sign, like in the case of migraine. Possible factors include alcohol consumption and excessive smoking. Exercise and physical activities may help; reduction of alcohol and smoking would be helpful too.
#4. A Tension Headache
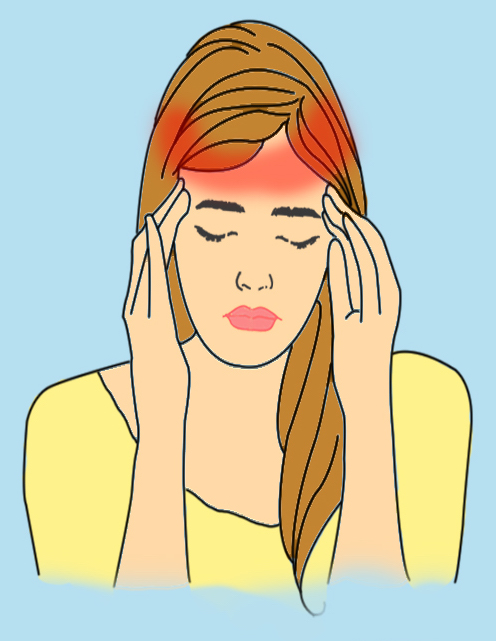

Symptoms of the tension-type headache include dull, non-throbbing pain across the sphere of the head. Tightness of the scalp or neck may accompany this pain. These occur one or two times per month on average to those who have episodic headaches. It may be caused by stress or a hidden depression. Short-term treatment will involve drugs and muscle relaxants prescribed by a doctor. Long-term treatment will involve learning relaxation techniques like meditation, quitting alcohol consumption and smoking, and learning more effective ways of coping with stress.
#5. Neck Pains
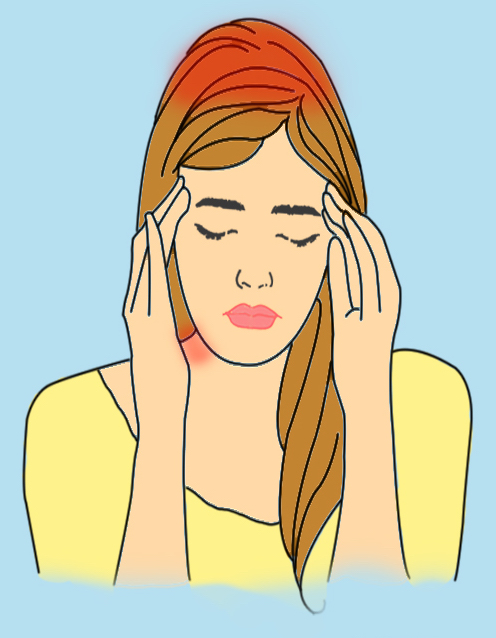

This pain is localized on the neck and nape. The pain gets worse when you move. It is caused by inflammation of the blood vessels of the head or bony changes in the structures of the neck. Short-term treatment will involve anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants prescribed by a doctor. Long-term prevention would require learning relaxation techniques and performing neck-muscle exercises.
#6. Migraine
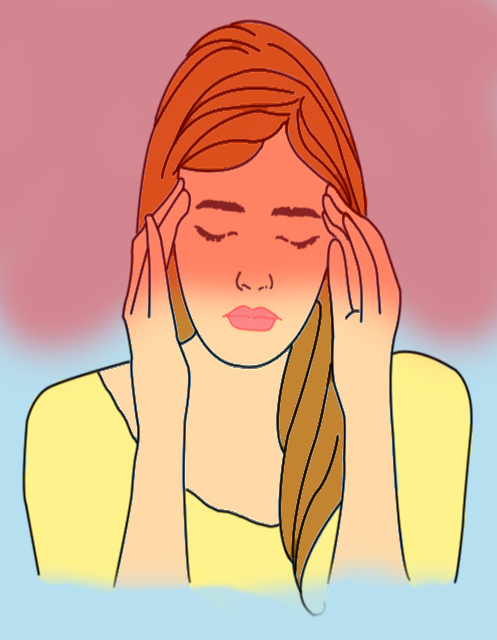

Severe, one-sided throbbing pain, often accompanied by nausea, cold hands, and sensitivity to sound and light means that you are having a migraine. The causes of migraines are not entirely understood, but genetics may play a role. Many factors can induce a migraine, like menopausal hormones, weather changes, stress, and a change in altitude, to name just a few.
A migraine attack can cause pains for several hours to days, and the pain can be quite disabling.
About one-third of people experience an aura before the start of a migraine, according to Medical News Today.
Migraines can occur in both adults and children. The attack frequency can be several times a week, or in some cases only once a year.
Short-term treatment will involve analgesics and anti-nausea medications prescribed by a medic. Long-term preventive methods will include regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and learning positive ways of coping with stressful situations.
Photo credit: Illustration – The Epoch Times
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.