Headache Pain: What to Do When Your Head Hurts
Most of us get headaches from time to time. Some are mild. Others cause throbbing pain. They can last for minutes or days. There are many types of headaches. How you treat yours depends on which kind you have.Headaches might arise because of another medical condition, such as swollen sinuses or head injury. In these cases, treating the underlying problem usually relieves headache pain as well. But most headaches—including tension headaches and migraines—aren’t caused by a separate illness. A headache may feel like a pain inside your brain, but it’s not. Most headaches begin in the many nerves of the muscles and blood vessels that surround your head, neck, and face. These pain-sensing nerves can be set off by stress, muscle tension, enlarged blood vessels, and other triggers. Once activated, the nerves send messages to the brain, and it can feel like the pain is coming from deep within your head. Tension headaches are the most common type of headache. They can cause a feeling of painful pressure on the head and neck. Tension headaches occur when the muscles in your head and neck tighten, often because of stress or anxiety. Intense work, missed meals, jaw clenching, or too little sleep can bring on tension headaches. Over-the-counter medicines such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen can help reduce the pain. “Lifestyle changes to relax and reduce stress might help, such as yoga, stretching, massage, and other tension relievers,” says Dr. Linda Porter, an NIH expert on pain research. Migraines are the second-most common type of headache. They affect more than 1 in 10 people. Migraines tend to run in families and most often affect women. The pain can be severe, with pulsing and throbbing, and can last for several days. Migraine symptoms can also include blurry vision and nausea. “Migraines are complex and can be disabling,” Porter says. Certain smells, noises, or bright flashing lights can bring on a migraine. Other triggers include lack of sleep, certain foods, skipped meals, smoking, stress, or even an approaching thunderstorm. Keeping a headache diary can help to identify the specific causes of your migraines. Avoiding those triggers or using prescription medications could help prevent or lessen the severity of future migraines. Be careful not to overuse headache medications. Overuse can cause “rebound” headaches, making headaches more frequent and painful. People with repeating headaches, such as migraines or tension headaches, are especially at risk. Experts advise not to take certain pain-relief medicines for headaches more than 3 times a week. A less common but more severe type of headache comes on suddenly in “clusters” at the same time of day or night for weeks. Cluster headaches may strike one side of the head, often near one eye, with a sharp or burning pain. These headaches are more common in men and in smokers. In rare cases, a headache may warn of a serious illness. Get medical help right away if you have a headache after a blow to your head, or if you have a headache along with fever, confusion, loss of consciousness, or pain in the eye or ear. “Know what kind of headache you have and, if you can’t manage it yourself, seek help,” Porter says. “Remember, there are preventive behavioral steps and medicines that can help manage headaches. But if the pain is severe or lasting, get medical care.”
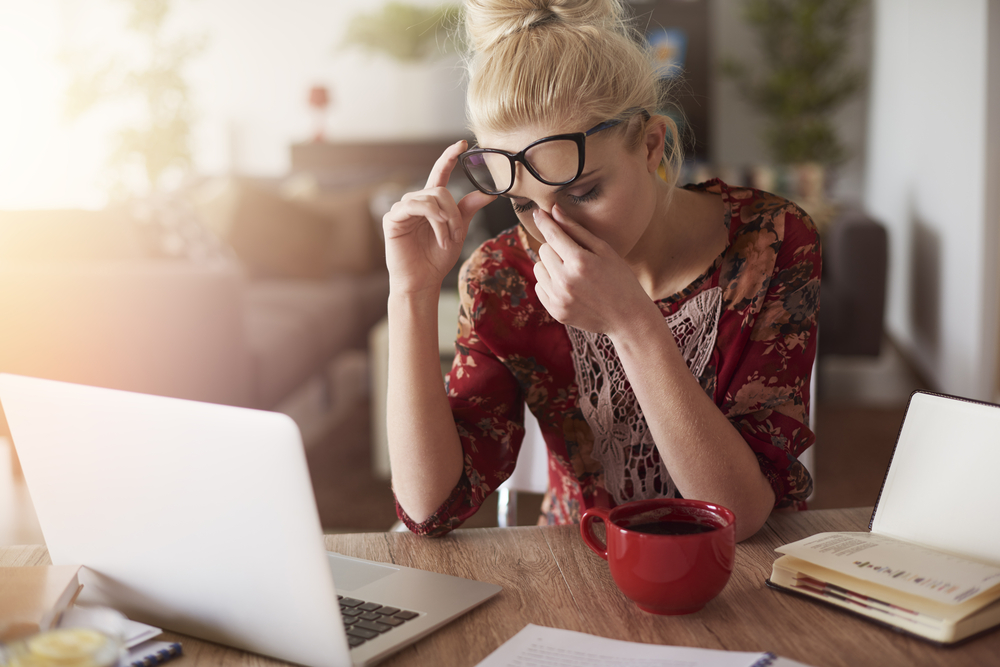

Most of us get headaches from time to time. Some are mild. Others cause throbbing pain. They can last for minutes or days. There are many types of headaches. How you treat yours depends on which kind you have.
Headaches might arise because of another medical condition, such as swollen sinuses or head injury. In these cases, treating the underlying problem usually relieves headache pain as well. But most headaches—including tension headaches and migraines—aren’t caused by a separate illness.
A headache may feel like a pain inside your brain, but it’s not. Most headaches begin in the many nerves of the muscles and blood vessels that surround your head, neck, and face. These pain-sensing nerves can be set off by stress, muscle tension, enlarged blood vessels, and other triggers. Once activated, the nerves send messages to the brain, and it can feel like the pain is coming from deep within your head.
Tension headaches are the most common type of headache. They can cause a feeling of painful pressure on the head and neck. Tension headaches occur when the muscles in your head and neck tighten, often because of stress or anxiety. Intense work, missed meals, jaw clenching, or too little sleep can bring on tension headaches.
Over-the-counter medicines such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen can help reduce the pain. “Lifestyle changes to relax and reduce stress might help, such as yoga, stretching, massage, and other tension relievers,” says Dr. Linda Porter, an NIH expert on pain research.
Migraines are the second-most common type of headache. They affect more than 1 in 10 people. Migraines tend to run in families and most often affect women. The pain can be severe, with pulsing and throbbing, and can last for several days. Migraine symptoms can also include blurry vision and nausea.
“Migraines are complex and can be disabling,” Porter says. Certain smells, noises, or bright flashing lights can bring on a migraine. Other triggers include lack of sleep, certain foods, skipped meals, smoking, stress, or even an approaching thunderstorm. Keeping a headache diary can help to identify the specific causes of your migraines. Avoiding those triggers or using prescription medications could help prevent or lessen the severity of future migraines.
Be careful not to overuse headache medications. Overuse can cause “rebound” headaches, making headaches more frequent and painful. People with repeating headaches, such as migraines or tension headaches, are especially at risk. Experts advise not to take certain pain-relief medicines for headaches more than 3 times a week.
A less common but more severe type of headache comes on suddenly in “clusters” at the same time of day or night for weeks. Cluster headaches may strike one side of the head, often near one eye, with a sharp or burning pain. These headaches are more common in men and in smokers.
In rare cases, a headache may warn of a serious illness. Get medical help right away if you have a headache after a blow to your head, or if you have a headache along with fever, confusion, loss of consciousness, or pain in the eye or ear.
“Know what kind of headache you have and, if you can’t manage it yourself, seek help,” Porter says. “Remember, there are preventive behavioral steps and medicines that can help manage headaches. But if the pain is severe or lasting, get medical care.”